Based on above, you can already tell there are many channels to measure your ROI. Hence, what is the ROI for a website. Facebook is a good example or social media in general. This is to invite fans and inform them of promotions. Blogs and twitter are another examples where the business owner can really promote services offered etc. Twitter is great since its basically an instant update. Media write ups are another category that greatly raise awareness.
Search Here!
Thursday, November 18, 2010
Website ROI
Based on above, you can already tell there are many channels to measure your ROI. Hence, what is the ROI for a website. Facebook is a good example or social media in general. This is to invite fans and inform them of promotions. Blogs and twitter are another examples where the business owner can really promote services offered etc. Twitter is great since its basically an instant update. Media write ups are another category that greatly raise awareness.
Wednesday, November 10, 2010
Coffee Cup
Our speaker talked about The Web Starter pack...this is the most basic CoffeeCup pack they offer, which allows people to create awesome websites without needing to do any coding!!! Its a good option for many people who are just getting started in web design. For people with more experience, the The Web Designer pack is the next level up...CoffeeCup also offers is the E-commerce pack, which has the shopping cart designer and other programs that are suitable to develop e-commerce websites.
Wednesday, November 3, 2010
Web Usability
1- Efficiency: The structure of the site should be efficient...
2-Task Flow: the flow is important as a usable site has a page flow that must match with the workflow.
3-Replication: It's ok to use templates!
4-Testing for usability: Testing early is very important within the design stage. A designer should not wait till the end to do this. HTML, Javascript should be tested for compatibility.
5-Motivation: The design for the website should meet the specific needs of the user. The design should motivate different types of users to specific parts of the site.
6-Track the traffic: Keep track of which page gets hit the most. Which page do people spend less time and click right onto the next page immediately? The site can be adjusted accordingly.
Webform Podcast
Wednesday, October 20, 2010
Visually Impaired and Web Accessibility
A large percent of Internet surfers are visually impaired. These individuals can be blind, colour blind or not have the vision they once had. It is very important for their needs to be recognized as well.
Macintosh Accessibility for the Visually Impaired
Wednesday, September 29, 2010
Use of Color on the Web

Some key questions to keep in mind while trying to choose the right colors could be:
· Who are your site’s potential visitors?
· What are your products or services?
· What are your site’s key objectives?
Text and background color selections do also affect readability, which can be an issue for visitors who are older those with visual impairments.
Check this site out for some great online color tools : http://bluefaqs.com/2009/11/25-online-color-tools-for-designers/
Thursday, September 9, 2010

Sites built to Web Standards
The term web standards can mean diverse things to different people. For some, it is ‘table-free sites‘, for others it is ‘using valid code‘. However, web standards are much broader than that. A site built to web standards should adhere to standards (HTML, XHTML, XML, CSS, XSLT, DOM, MathML, SVG etc) andpursue best practices (valid code, accessible code, semantically correct code, user-friendly URLs etc).
In other words, a site built to web standards should ideally be lean, clean, CSS-based, accessible, usable and search engine friendly.
http://www.maxdesign.com.au/articles/checklist/
Why do web standards matter?
There are numerous advantages to using web standards. Here are some highlights:
• Save $$$ (ease of maintenance): It is quick and easy to change unformatted content in HTML files which indicates that site changes take less time and eventually less money.
• Up to 60% Less Code! : Many websites that are built around Web Standards use up to 60% less code.
• Improved Search Engine Rankings
• Changing the layout is easier: When the site is designed with web standards in mind, site-wide changes become a lot easier. If a different color is needed for the site, all that needs to be done is to change one line of code in CSS. If you want your website to look good on mobile devices all that needs to be done is use CSS and your website will look good on mobile devices . Designing with web standards will give many more options to select from and will allow for swift and effortless site-wide changes.
• Accessibility: Vision impaired surfers may be using special web browsers. Using web standards makes it much easier to make content useable under special circumstance and also to the search engines.
Thursday, September 2, 2010
What is Information Architecture?
For instance, a well architected website selling Caribbean cruises would branch into sub-topics (sub-directories and/or sub-menus) that flesh out the main theme. These sub-areas of the site might focus on specific Caribbean ports of call, cruise lines, specials / deals, thematic cruises, local culture, and anything else relevant to Caribbean cruises.
(Information above was located at http://www.ozonesem.com/search-engine-optimization/website-structure.html)

I have always wanted to know more about how the domain structure for multilingual sites are. Upon visiting some good sites, I figured that there are many ways to handle sites that are created in different languages for these countries. It looks like the best method however, is to create country specific TLDs with unique sites and content. Localization is critical and ensure that for instance the Spain site has language specific to Spain, not Chile! Another comparable method is to create sub-domains for each language version. Another not quite desirable, is to create a directory structure that serves each language. In all cases, web writers need to make sure of the name of the directories that use the language of the country being served.

Thankfully, Google Webmaster Tools now permit us to indicate the language preference for directories and sub-domains.
The first method, of course, has many benefits, which include the ability to validate the domain in Google Webmaster Tools and specify the geographic location. International TLDs will be indexed and listed in specific language versions of search engines and regional directories, while many sub-domains and directory localization strategies will not be indexed and listed such.
Small international sites should be served with a version selector for each country-specific domain. This assists with spidering and allows users to choose the version of the site they are interested in using.
Thursday, August 26, 2010
Writing for the Web

Chapter 5 begins with stating the differences between writing for print vs. web. It is interesting to see that being a good web writer isn’t that hard. Web writers need to be very cautious since people read differently online. As a Web writer - you better have the information the website visitor is looking for or else the reader will leave the site and will never come back! Here is a list of few techniques a web-writer can use to increase traffic and engage readers – after all, according to the authors of this book, good web writing is useful, usable, engaging and findable :
• Writing has to be easy to scan A lot of testing has been done on how long it takes for the average web surfer to decide if they are going to “bother” to read a web page, or just click away. The actual numbers vary, but are in the range of three to five seconds. It’s your job to present information in such a way that you can get the attention of your reader, and let them know that this is where to find the information they’re looking for – or not as the case may be.
• Avoid the passive voice
Get to the point immediately!!!
• Context needs to be there
If your information is being distributed via RSS, there should be enough context when not viewed in its original location.
• Good titles for the page and for any subsections
Descriptive titles are the key. This will direct the reader to find the information they are looking for a whole lot faster/descriptive title is used, it’s much easier for the reader to find the information they are looking for, especially if the information is being viewed out of context. It also helps out with the search engines.
• Tools, Process and Team
These are the top things needed to focus on having prior to even starting to write.
• Regular Updates for fresh information
People need to see new information to even be motivated to check the website out and revisit !
During class last time, we browsed the web and saw both great and poorly designed websites. It was interesting to point out the errors and what made us frustrated about the bad sites! All web writers need to keep in mind what would make a pleasant experience for the web users.
Monday, April 26, 2010
ITIL
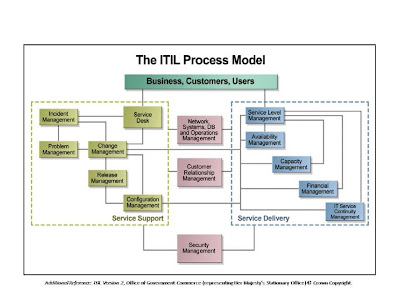
ITIL Overview (http://www.benchmarklearning.com/COMMUNITIES/ITIL/ITIL.aspx)
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a comprehensive, non-proprietary and publicly available set of guidelines for "best practice" in IT service management, owned by the British Office of Government Commerce (OGC). Each library module provides a code of practice intended to improve IT efficiencies, reduce risks and increase the effectiveness and quality of IT services management and infrastructure. ITIL has recently undergone a refresh and the newly published ITIL v3 core books have adopted an integrated service lifecycle approach to IT Service Management.
What is ITIL All About?• A set of specialized organizational capabilities for providing value to customers in the form of services.
• A set of best practices—not a methodology
• Providing guidance, not a step-by-step how-to manual
• Providing optimal service provision at a justifiable cost
• A non-proprietary set of best practices—public domain
ITIL often relies on the skills of the Project Manager and the Business Analyst to ensure project success
2. A more detailed summary of ITIL Service Desk
ITIL Service Desk (http://www.educause.edu/wiki/ITIL+Service+Desk)
The Service Desk is critically important as the very first contact the organization's users have with IT Services. The Service Desk is a single point of contact for end users who need anything from IT. The Service Desk handles day-to-day customer issues, end-user calls, and related service issues. The Service Desk is NOT just a call center or expanded help desk. IT offers a broader range of services through a more global approach to IT. Not only can a Service Desk handle incidents, problems and questions, but a Service Desk can also provide an interface for other activities such as customer change requests, billing and availability management. The Service Desk has great strategic importance. It represents the interests of the customer to the rest of the IT organization, and is the most important function in an organization for many customers. Because of this, the Service Desk helps to ensure the delivery of customer satisfaction - the key measurement of effective IT Services Management. Some important parts regarding the ITIL-based Service Desk:
• Provides a single point of contact (SPOC) for customers and users
• Facilitates the restoration of normal operational service
• Is the front door for other IT departments
• Deals with many customer queries without needing to contact specialist personnel
• Follows up calls originating from within the IT organization
• Detects incidents
• Verifies the details of a caller and their IT resource (also called a configurable item, or CI)
• Always acts professionally when dealing with users
• Ensures that users do not have to search endlessly for a solution
• Is consistent and efficient in all customer contacts
• Serves as the main source of information to users
• Provides information about new and existing services, provisions of Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and order procedures and costs
• Performs backups and restores, provides LAN connections, allocates disk space change requests, creates accounts, authorizes and changes passwords (i.e., "standard changes")
• Has access to a knowledge base, which will contain a list of known solutions for common incidents
• Is responsible for keeping the customer informed on the status of their request
• Is a centralized function for incident and request handling
• Performs ongoing monitoring and management of customer satisfaction
• Provides strong levels of incident communications and ownership
• Has staff and management with the right level of support and customer care skills
• Ensures long term customer retention and satisfaction
• Assists in the identification of business opportunities
• Reduces support costs by the efficient use of resource and technology
• Provides advice and guidance to customers
• Communicates and promotes IT services
3. A profile of an ITIL consulting company - what is their pitch, what services, discuss one reference client from their website.
TDG CONSULTING
For many enterprise organizations in the Southeast, TDG is the natural choice to deliver cost-effective, comprehensive, compelling, and creative IT Service Management services.
TDG provides practical ITIL consulting, mentoring, and training - all across a variety of offerings, engagements, and scenarios.
Services
Many organizations understand that they need some type of assistance, but they are unsure of what type, when, and why. Furthermore, many have been burned by too much consultancy or ITSM services of the wrong type, or in the case of ITIL assistance, consultancy that forced a 'vanilla' version of ITIL without regard to organizational uniqueness.
TDG recognizes and, frankly, encourages each organization to adapt ITIL disciplines to their specific IT culture.
The TDG set of ITSM service offerings ranges from fixed price assessments, implementation assistance, focused workshops, and ITIL certification training. Each offering is geared towards a certain point in an organization's implementation timeline.
In order to determine where potential clients would fall on this process improvement trajectory, TDG recommends their clients use an IT process improvement timeline which represents the various phases most organizations will encounter as they move from the early state of pre-ITIL awareness to one where ITIL disciplines are interwoven in the fabric of day-to-day IT Operations. I found this timeline interesting. Please see below:

Reference Client Example
Checkfree Corporation
Reference: David Bryant
Title: Senior Manager
Location: Atlanta, GA
"CheckFree engaged TDG to conduct a strategic assessment of several ITIL and non-ITIL processes at CheckFree. This engagement involved interviewing all senior and executive IT management, conducting a process-specific maturity assessment based on the CMMI , investigating all evidentiary support for process tasking, documenting necessary cultural barriers to change, performing a detailed SWOT analysis, assembling budgeting and cost payback figures, and developing a 3,000 line-item project plan.
Based on the final report delivered by TDG, CheckFree decided to launch a rollout of the ITIL Service Management processes in its key operating environments. In their capacity as coaches, consultants, ITIL educators, content developers, training collateral and process engineers, TDG led the CheckFree ITIL team through a multi-phased deployment methodology.
TDG was an invaluable partner in the ITIL rollout at CheckFree and I would highly recommend them to other companies who are transitioning to ITIL. TDG's knowledge, expertise, and technical competency sets them apart from other consultants."
4. Find an ITIL software tool and briefly describe the service desk functionality.
(http://www.numarasoftware.com/#1)
I did research on Numara Software, which has a software tool called Numara Footprints for service desk management and the Numara Asset Management Platform (NAMP) for IT asset management. By relying on a single vendor to automate and manage all types of service requirements and processes, including those beyond IT, their clients deliver world-class support. With a low cost of ownership and a practical approach, Numara Footprints is fast to implement, simple to use, easy to scale, and inexpensive to own.
"With its unique "multi-project" architecture, Numara Footprints enables it’s clients to manage service desk processes from a single integrated platform – minimizing overhead and increasing service delivery quality. Automating and consolidating processes, such as internal and external customer service, facilities management, and HR simultaneously helps clients reduce complexity and the support burden. Numara FootPrints puts instant changes and customizations in the hands of the service management team, not expensive programmers or consultants. Numara FootPrints helps service management organizations "do more with less" by requiring fewer resources to design, implement, adapt, manage, and report on multiple services and business processes. With zero programming and no extensive consulting engagement required for implementation and customization, Numara FootPrints gives IT and support groups control and reduces cost of ownership."
Tuesday, April 20, 2010
Software Design Patterns & Christopher Alexander
After spending some time researching what design patterns actually were, I found out that a professor in architecture from Berkley, launched the California answer to the problem of design complexity in 1977. This professor was Christoper Alexander. His theory was explained in three books: The Timeless Way of building (1979), A Pattern Language: Towns, Buildings, Construction (1977), and The Oregon Experiment (1975).

Patterns originated as an architectural notion by Christopher Alexander. So, what are patterns and their languages and what did Christopher Alexander have to do with this? Patterns and pattern languages for describing patterns are ways to explain good designs, describe best practices, and capture experience in a way that it is promising for others to reprocess this experience. In addition to the patterns, Alexander defined a set of rules e.g. a pattern language in which patterns could be meaningfully combined. Design pattern or computer science are extensively used by software engineers for the actual design process as well as for communicating a design to others.
According to an article on http://www.opensecurityarchitecture.org/cms/definitions/security_patterns,today we find patterns for many different areas in IT such as design patterns, architectural patterns and interaction design patterns but also security patterns. All these patterns use very similar pattern languages. It is interesting to observe how close all these pattern languages stick to the original language proposed by Christopher Alexander. The central argument of the Pattern Language is that, in the face of complexity, humans have evolved archetypal designs, which solve recurrent problems. These solutions are called patterns. In primitive societies, birds and humans had ways of using mud and grass to make dwellings. They remained constant from generation to generation. In modern societies, a greater range of patterns is available. Yet, the Pattern Language argues, there are still ways of doing things that, over an endless period of time, have satisfied complex human requirements. An ancient example is finding a choice location for an outdoor seat. Neglect of this pattern has led to a modern tragedy. Most outdoor seats in most towns are woefully sited: their locations are unprotected, isolated, noisy, windy, claustrophobic, too hot or too cold. The ancient pattern was to place a seat near a tree, with its back to a wall, in a sunny position with a good view (Figure 3.4). The archetype for this solution balances prospect with refuge. Jay Appleton, in The Experience of Landscape, sees this as a fundamental human need: it satisfies human desires for safety, comfort and a good vantage point ( Appleton, 1975). To avoid blunders, planners and designers must have this information.
Types of Design Patterns (http://geekexplains.blogspot.com/2008/09/design-patterns-types-and-suggested.html)
Design Patterns are divided into 3 categories:
• Creational - the design patterns belonging to these category are used for creating objects. Using such a design pattern provides more flexibility where we require a control over the creation of objects. One very common use case is the usage of a creational design pattern to restrict the total number of instances of a class. Example: The Singleton Pattern, The Abstract Factory Method Pattern, etc
• Structural - as the name suggests this category groups all those design patterns which help the user to group objects into larger structures to meet the complex requirements in a structured way. A common use case is to use such a design pattern for designing a complex user interface. Example: The Adapter Pattern, The Proxy Pattern, etc.
• Behavioral - the patterns belonging to this category are used to define communication between objects of a proposed solution. In other words such design patterns helps defining the flow of a complex system. Example: The Chain of Responsibility Pattern, The Strategy Pattern, The Iterator Pattern, etc
Example of a Creational Design Pattern: The Abstract Factory Method Pattern
I found the following example from the A&P Web Consulting Company and easily understood the Abstract Factory Pattern through this page.
http://www.apwebco.com/gofpatterns/creational/FactoryMethod.html#example
Definition
Define an interface for creating an object, but let subclasses decide which class to instantiate. Factory Method lets a class defer instantiation to subclasses.
Class Diagram

Factory Method pattern is a simplified version of Abstract Factory pattern. Factory Method pattern is responsible of creating products that belong to one family, while Abstract Factory pattern deals with multiple families of products.
The official GoF Factory Method UML diagram (above) can be represented as in diagram below which uses the same terminology as Abstract Factory UML diagram:

Participants
Product
• defines the interface of objects the factory method creates.
ConcreteProduct
• implements the Product interface.
Creator
• declares the factory method, which returns an object of type Product. Creator may also define a default implementation of the factory method that returns a default ConcreteProduct object.
• may call the factory method to create a Product object.
ConcreteCreator
• overrides the factory method to return an instance of a ConcreteProduct
Benefits
• Eliminates the needs to bind application classes into your code. The code deals with interfaces so it can work with any classes that implement a certain interface.
• Enables the subclasses to provide an extended version of an object, because creating an object inside a class is more flexible than creating an object directly in the client.
Usage
• When a class cannot anticipate the class of objects it must create.
• When a class wants its subclasses to specify the objects it creates.
• Classes delegate responsibility to one of several helper subclasses, and you want to localize the knowledge of which helper subclasses is the delegate.
Here is another representation of the Abstract Factory Design Pattern:

References
[1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A_Pattern_Language
[2] http://natureoforder.com/library/scientific-introduction.pdf
[3] http://www.opengroup.org/security/gsp.htm
[4] http://www.securitypatterns.org
[5] http://www.gardenvisit.com/history_theory/library_online_ebooks/architecture_city_as_landscape/development_alexanders_pattern_language#ixzz0leOU2AYz
[6] http://www.apwebco.com/gofpatterns/creational/FactoryMethod.html
[7] http://geekexplains.blogspot.com/2008/09/design-patterns-types-and-suggested.html
[8] http://www.apwebco.com/gofpatterns/creational/FactoryMethod.html#example
[9] http://www.opensecurityarchitecture.org/cms/definitions/security_patterns
Monday, February 8, 2010
What is Oslo ?!
Oslo is a Microsoft model-driven application development platform intended to allow non-developers to build distributed applications. The initial version of Oslo won’t let a complete novice build applications, but it will ease development. According to eweek,The visual tooling for Oslo was known as Quadrant, the language was known as M and the repository, though unnamed, was based on Microsoft SQL Server. This was Microsoft's messaging leading up to the 2008 PDC (Professional Developers Conference), which took place in October 2008.
“The business analyst is an under-served role, and a good opportunity for the product,” said Brad Lovering, a Microsoft technical fellow leading the Oslo effort. Don Box, a partner architect at CSD who is working on the Oslo language stack, added, “We’re trying to make it simple to get an idea out of your brain and onto a hard disk.”
The Oslo tool allows users to capture domain knowledge in domain-specific views. The tool also will be useful for more advanced diagramming, such as enabling the development of BPMN (business process modeling notification) workflows and UML (Unified Modeling Language) services. (Eweek)
I believe this is an absolutely great tool because people who are less experienced in modeling will deal with a less complex, more automotive and inclusive process. Oslo will also change who can develop applications, what sorts of applications can be modeled and how quickly new applications can be modeled. Less experienced developers would definitely benefit from such a tool. Oslo makes it easier for people to write things down in ways that make sense for the domain they are working in. In other words, you can be a programmer without knowing it !
Monday, January 18, 2010
Google Adwords
Google Adwords does this by using the placed text ad that appears when someone searches for phrases that are related to one's products and services - and they ultimately display as a sponsored link. The way Google Adwords works is under a pay per click basis and you only pay the amount per person clicking on your ad (that you have initially bid for per click) as a result of a web search.
These ads are in text format and consist of a title line followed by two short descriptive lines afterwards and additionaly have a URL link to a website or a specific website page.
These ads will be shown on results page that the customer wants them to appear in.
Here is a process model showing Google AdWords from the customers perspective that I have created:




